In the realm of aquaculture, efficient oxygenation and water circulation are paramount for fostering a healthy aquatic ecosystem. One of the most widely utilized systems for achieving these objectives is the Paddle Wheel Aerator. According to a report by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), aquaculture has expanded significantly over the past few decades, and with this growth, the need for robust aeration systems has become increasingly critical. Paddle Wheel Aerators are popular owing to their ability to enhance oxygen transfer efficiency, which is essential in supporting fish growth and improving overall water quality.
Selecting the right Paddle Wheel Aerator involves understanding specific aquaculture needs, including pond size, water depth, and species being cultivated. Research indicates that improper aeration can lead to suboptimal growth conditions, with studies showing that oxygen levels below 5 mg/L can severely affect fish health and productivity. By carefully evaluating performance metrics, such as aeration capacity and energy consumption, aquaculturists can optimize their oxygenation strategies. Thus, making informed choices about Paddle Wheel Aerators not only directly impacts productivity but also contributes to sustainable aquaculture practices, aligning with industry goals to enhance efficiency and promote environmental stewardship.


Paddle wheel aerators play a crucial role in aquaculture systems by enhancing oxygen levels in water bodies, which is essential for maintaining healthy fish and shrimp populations. These devices facilitate the mixing of water, which results in better oxygen distribution and helps to control harmful substances, such as ammonia and carbon dioxide. According to a report by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), adequate oxygen levels are necessary for optimal growth rates in aquatic species, making the choice of aerator vital for successful aquaculture.
When selecting the right paddle wheel aerator, it’s important to consider factors such as water depth, surface area, and the specific species being cultivated. For instance, Shrimps typically require higher oxygen levels than some fish species, thereby necessitating a more robust aeration system. Additionally, understanding the efficiency and maintenance needs of paddle wheel aerators can significantly impact operational costs and sustainability. According to a recent study, properly maintained aerators can improve water quality and reduce feed conversion rates by up to 10%, enhancing overall production efficiency.
Tips: Always assess the specific aeration requirements of your aquatic species. Monitor dissolved oxygen levels regularly and adjust aerator operation accordingly to maintain ideal conditions. Investing in quality paddle wheel aerators tailored to your aquaculture setup can lead to better growth outcomes and more sustainable production practices.
When selecting a paddle wheel aerator for your aquaculture needs, several key factors must be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and health of your aquatic systems. One critical consideration is the water depth of your facility. Studies show that paddle wheel aerators are most effective in environments where the water depth ranges from 1 to 2 meters. In these conditions, the aerators can facilitate sufficient water circulation and promote oxygen transfer, essential for the survival of fish and other aquatic organisms.
Another important factor is the aeration capacity required for your specific application. According to a report by the Aquaculture Research Institute, the aeration demands can vary significantly based on the species of fish being cultivated and the rate of biomass stocking. It is recommended to calculate the necessary oxygen transfer rate, which typically averages around 0.5-1.0 kg of oxygen per hour for every 1000 kg of fish biomass. Additionally, consider the energy efficiency of the aerator; paddle wheels are known for their relatively low energy consumption compared to other aeration systems, which can lead to lower operational costs, making them a cost-effective option for aquaculture facilities.
Lastly, environmental factors such as water temperature and flow patterns should also be evaluated. Research indicates that warmer water temperatures can increase the demand for oxygen, hence adequate aeration becomes even more critical. Understanding the ecological requirements and how paddle wheel aerators can meet these needs is essential for maintaining a healthy aquaculture environment.
Paddle wheel aerators are essential in enhancing the oxygen levels in aquaculture systems, significantly influencing the growth and health of aquatic organisms. Different types of paddle wheel aerators cater to varying aquaculture needs. For instance, surface paddle wheel aerators are commonly used in ponds where they help in mixing and aerating water efficiently. According to a report by the Aquaculture Association, these aerators can increase dissolved oxygen levels by 2-5 mg/L, which is critical for fish respiration and overall ecosystem balance.
In contrast, submersible paddle wheel aerators are ideal for deeper water bodies, promoting oxygen distribution at various depths. This type of aerating system is particularly beneficial in larger aquaculture setups, as it helps mitigate issues related to stratification, where oxygen levels vary significantly with depth.
Research conducted by the Journal of Aquaculture suggests that these aerators can enhance water circulation and reduce harmful gas buildup, ultimately leading to improved fish production rates. By selecting the appropriate type of paddle wheel aerator, aquaculture farmers can optimize their operations and ensure a healthy environment for their stock.
When evaluating aeration needs for aquaculture, it is vital to consider both water volume and stocking density. The American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers (ASABE) recommends that a well-aerated system should achieve a dissolved oxygen level of at least 5 mg/L, critical for the health of aquatic species. As a rule of thumb, to maintain this level, it is suggested that ponds with a water volume of 1 acre and a depth of 4-6 feet require around 1-2 horsepower of aeration per acre for optimal fish growth.
Stocking density also plays a crucial role in determining aeration requirements. According to research published by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), higher densities lead to increased oxygen consumption and, consequently, a greater need for effective aeration. For instance, stocking fish at 10,000 per acre results in an oxygen demand that can rise to 0.5 mg/L per month, necessitating robust aeration systems to sustain healthy living conditions. Evaluating these factors will not only ensure compliance with aquaculture best practices but also enhance yield and reduce mortality rates among fish populations.
| Water Volume (m³) | Stocking Density (kg/m³) | Recommended Aerator Size (HP) | Aeration Rate (kg O₂/h) | Efficiency Rating (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 50 | 85 |
| 1000 | 1.5 | 3.0 | 100 | 80 |
| 2000 | 2.0 | 5.0 | 200 | 75 |
| 5000 | 3.0 | 7.5 | 400 | 70 |
| 10000 | 4.0 | 10.0 | 800 | 65 |
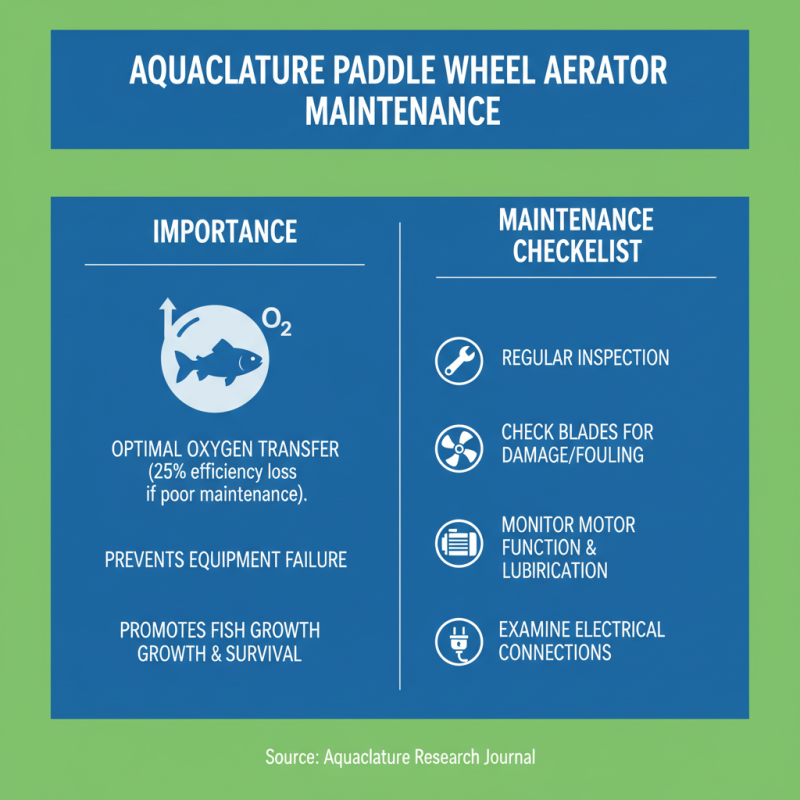
When selecting paddle wheel aerators for aquaculture, maintenance and operational considerations play crucial roles in ensuring effective performance and longevity. Regular maintenance not only prevents equipment failure but also optimizes aeration efficiency, which is vital for maintaining healthy aquatic environments. According to a study published in the Aquaculture Research Journal, poorly maintained aerators can lead to a 25% decrease in oxygen transfer rates, significantly affecting fish growth and survival rates. Implementing a routine checklist for maintenance tasks, including inspection of blades, motor functionality, and electrical connections, can prevent such declines in efficiency.
Operational considerations are equally important, as they directly impact the overall aeration process. Factors such as the water body size, depth, and contamination levels should dictate the operational parameters set for the paddle wheel aerators. Research by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration indicates that optimizing aerator operation times can enhance oxygen saturation levels by up to 35% under varying environmental conditions. Additionally, adjustments to the paddle angle can influence water circulation patterns, further improving oxygen distribution in aquaculture settings. By carefully considering these maintenance and operational factors, aquaculture operators can ensure that their paddle wheel aerators function effectively, fostering a healthier ecosystem for aquatic life.