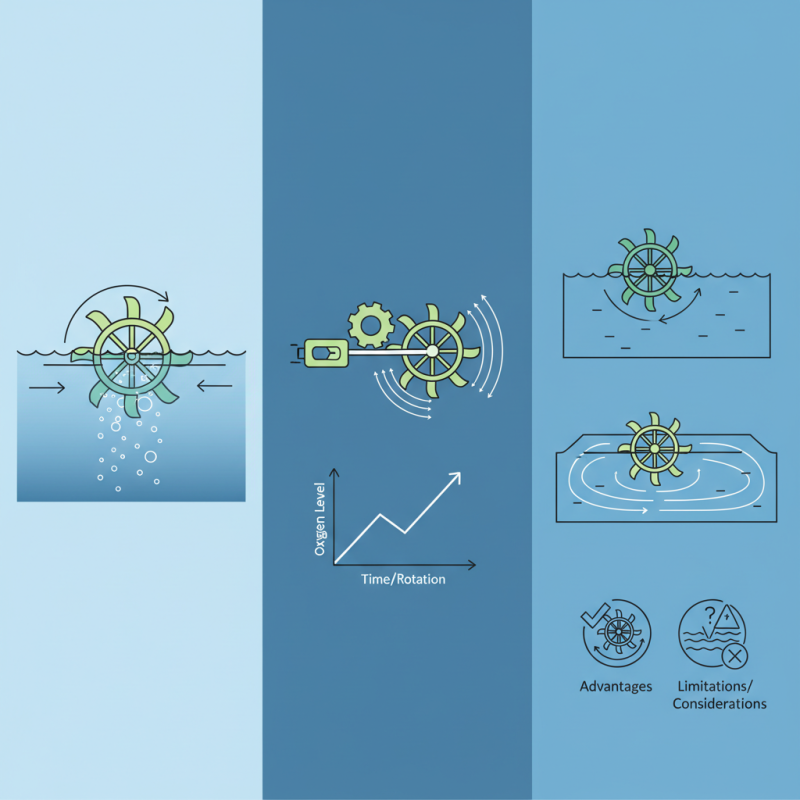
A Paddle Wheel Aerator is a vital tool in aquaculture and wastewater management. It enhances water quality by increasing oxygen levels. The design consists of large blades fixed to a wheel that rotates in the water. This movement causes bubbles to form and rise to the surface.
Understanding how a paddle wheel aerator works requires observing its mechanics. As the wheel turns, it pulls water in and pushes it back out. This process helps in mixing water and ensuring a uniform distribution of oxygen. However, one must reflect on its limitations. This type of aerator may not be suitable for all water bodies. Its efficiency can vary based on depth and current.
By learning about the Paddle Wheel Aerator, one can appreciate its role in maintaining healthy aquatic environments. Yet, it’s important to consider alternative methods. Each technique poses its own advantages and challenges. Evaluating these options can lead to better water management practices.
Paddle wheel aerators play a crucial role in aquaculture. They are used to increase water oxygen levels, benefiting aquatic life. These devices stir the water, helping to enhance gas exchange. Studies show that effective aeration can boost fish growth by up to 30%. Proper oxygenation prevents fish stress and promotes a healthy environment.
One key aspect is to maintain optimal water circulation. Poor circulation can lead to dead zones, which harm fish. Paddle wheel aerators can help mitigate this by keeping water moving. For best results, owners should monitor oxygen levels regularly. This simple step can lead to significant improvements in fish health and growth.
Tips: Consider adjusting the paddle speed based on water temperature. Warm water holds less oxygen. Additionally, check for any debris that might hinder the aerator's performance. Regular maintenance is essential for efficiency.
Paddle wheel aerators are commonly used in aquaculture and wastewater treatment. They consist of several key components that work together to improve water quality. The main part is the paddle wheel itself. It typically has several large paddles attached to a rotating axis. These paddles create turbulence in the water, which helps facilitate oxygen transfer.
In addition to the paddle wheel, the aerator includes a driving mechanism and a supporting frame. The driving mechanism often consists of an electric motor or a gear system. It ensures the paddles rotate smoothly and efficiently. The supporting frame holds everything in place and provides stability during operation.
While these aerators are effective, they may not be perfect. Sometimes, the paddles can get clogged with debris. This can reduce their efficiency. Regular maintenance is necessary to ensure optimal performance. Pond conditions may also affect how well they work. Therefore, monitoring and adjustments are essential for achieving the best results.

Paddle wheel aerators are essential for improving water quality in various aquatic environments. They mix water while introducing oxygen. This process enhances aerobic conditions, which are vital for fish health and overall ecosystem balance. Studies show that these aerators can increase dissolved oxygen levels by 50% or more, significantly benefiting aquatic life.
Moreover, paddle wheel aerators help in nutrient management. They minimize stratification in deeper water layers. When water mixes, it helps distribute nutrients evenly. This can lead to better plant growth and a healthier habitat for organisms. However, improper use can cause turbulence that displaces organisms. This is an area needing attention.
According to industry reports, properly managed aeration can reduce harmful algal blooms by up to 30%. But, if miscalculated, these systems might not function effectively. The ideal aerator design depends heavily on specific water conditions and intended use. Monitoring and adjustments are crucial for maintaining efficiency and water quality.
Paddle wheel aerators play a crucial role in enhancing water quality in ponds and lakes. These devices circulate water and increase oxygen levels. Efficiency ratings often determine their effectiveness. However, several factors can impact performance metrics. The design, size, and motor power all contribute to overall efficiency.
In practice, pwaddle wheel aerators vary widely in their operational efficiency. Some may underperform in shallow waters, while others excel. This discrepancy can frustrate users seeking uniform results. Additionally, environmental conditions affect how well these aerators work. Temperature and water depth are significant variables.
Measuring performance is not always straightforward. Observing changes in aquatic life can provide insights. Sometimes, aerators fail to meet expectations. Users may need to adjust their strategies over time. Enthusiasts often debate the best approaches, sharing their experiences in community forums. Composite metrics can help in evaluating performance, yet they don't capture every angle. Testing under real-world conditions remains vital for optimization.
Paddle wheel aerators have significant applications across various industries. They are primarily used in aquaculture, wastewater treatment, and even in recreational ponds. In aquaculture, these devices help maintain optimal oxygen levels. This is crucial for the healthy growth of fish and other aquatic organisms. In wastewater treatment, they assist in the breakdown of organic materials, improving water quality.
In recent statistics, it's noted that over 60% of aquaculture operations utilize paddle wheel aerators. Their efficiency in oxygen distribution stands out. In industries, they can enhance the overall productivity of aquatic systems. Their ability to mix and aerate water is a vital factor in maintaining biodiversity in artificial environments.
Tip: Regular maintenance is essential for optimal performance of paddle wheel aerators. Without proper care, efficiency can decrease significantly. Monitor the aerator’s performance frequently to catch any issues early.
Another consideration is the impact of positioning. The placement of aerators can influence water circulation patterns. Incorrect positioning may result in dead zones in large bodies of water. Adjusting their location based on water flow can help mitigate these problems.