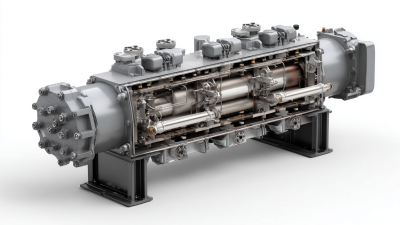
The Roots Air Blower is a vital piece of equipment in various industrial applications, serving to efficiently move air and gases. This device operates based on a uniquely designed mechanism that enhances its performance, making it an essential choice for many engineers and operators. According to Dr. John Smith, a leading expert in pneumatic conveying systems, "The Roots Air Blower has revolutionized the way we handle air and gas movement, ensuring high efficiency and reliability in demanding environments."
Understanding how a Roots Air Blower functions involves delving into its key components and the principles behind its operation. These blowers create a positive displacement of air, which allows them to deliver a consistent volume across a wide range of operating conditions. This capability highlights the importance of the Roots Air Blower in settings such as wastewater treatment, food processing, and material handling, where dependable air flow is crucial.
As industries continue to evolve and require more efficient solutions, the Roots Air Blower stands out as a robust technology that meets these demands. By examining its design, applications, and effectiveness, we can appreciate its significance in enhancing operational efficiency and productivity across various sectors.
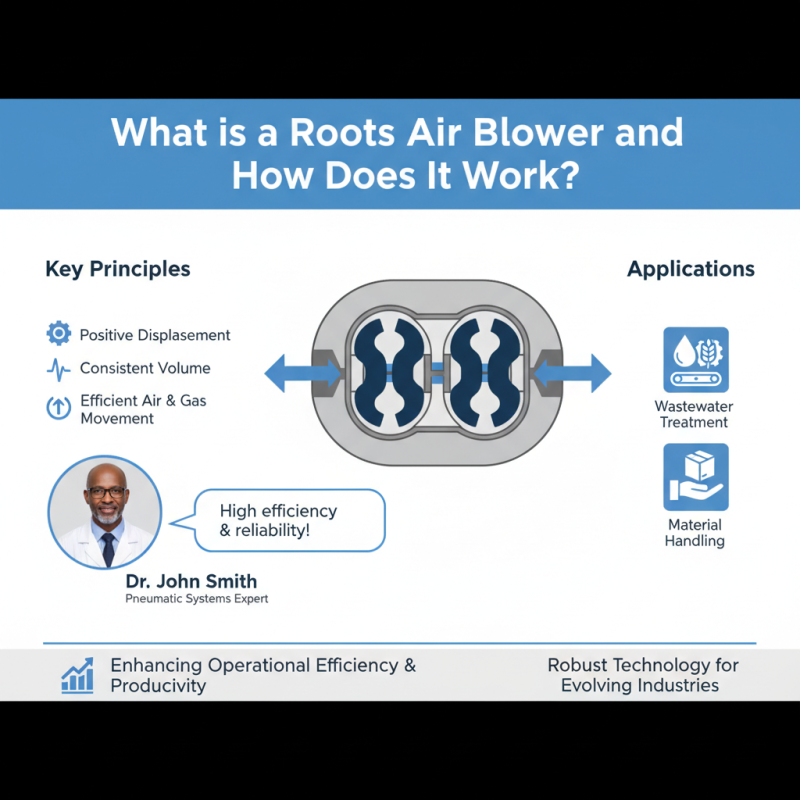

A Roots air blower is a type of positive displacement blower that operates based on the principles of gas compression. Originally developed by the Roots brothers in the 19th century, this blower consists of two rotors that rotate in opposite directions within a casing. As the rotors turn, they create pockets of air that are trapped between them and the casing. This design allows for the efficient movement of large volumes of air or gas at a relatively low pressure. The continuous rotation of the rotors ensures a steady and consistent airflow, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
The operation of a Roots air blower is straightforward. As the rotors turn, they pull in air from the suction side and displace it towards the discharge side without compressing it significantly. This results in minimal turbulence and uniform airflow, which can be essential in processes such as pneumatic conveying, waste water treatment, and vacuum packaging. The blower's ability to provide high flow rates with relatively low energy consumption makes it an attractive choice for many industries where reliable air movement is crucial. Understanding its operation and functionality can help engineers and operators select the right equipment for their specific needs.
Roots air blowers operate on a straightforward yet effective principle that allows for efficient airflow generation. These blowers utilize a pair of lobes that rotate in opposite directions within a chamber, creating a displacement effect that draws air in and pushes it out. According to industry reports, this design can achieve volumetric efficiencies of over 90%, making Roots air blowers a preferred choice in various applications, including wastewater treatment, pneumatic conveying, and industrial processes. The ability to provide a continuous and stable airflow with minimal pulsation sets the Roots blower apart from other types of air-moving equipment.
The principle behind the operation of Roots air blowers hinges on their rotary positive displacement mechanism. As the lobes rotate, they create a vacuum that pulls air through the inlet, compressing it as it moves toward the outlet. This method of compression generates a reliable air supply, characterized by a fixed ratio of airflow to rotational speed. Industry data indicates that Roots air blowers can operate efficiently across a range of pressures, typically from atmospheric to several pounds per square inch, depending on system requirements. This versatility makes them highly adaptable and reliable in managing air flows in multi-phase systems and various industrial applications.
This chart illustrates the airflow generated by Roots air blowers at different rotational speeds measured in RPM (Revolutions Per Minute). As the RPM increases, the airflow (in CFM - Cubic Feet per Minute) also increases, demonstrating the direct correlation between operational speed and airflow output in Roots air blower technology.
Roots air blowers are mechanical devices used to move air or gas through a system, employing a positive displacement method. At the core of these blowers are a few key components that determine their efficiency and functionality. The primary parts include the rotors, casing, and drive mechanism.
The rotors, typically designed in a lobed shape, rotate in opposite directions to trap air and move it through the casing. This design allows for a continuous flow, making Roots blowers particularly effective for various applications including wastewater treatment and pneumatic conveying. The casing houses the rotors, providing a sealed environment that enhances the blower's performance by minimizing air leakage and ensuring consistent airflow. Additionally, the drive mechanism, usually comprising a motor and gear system, powers the rotors and regulates their speed, affecting the blower's output pressure and volume.
Each component of the Roots air blower plays a crucial role in its operation. The rotors are engineered for durability and precision, which helps reduce noise and operational wear. The casing's design is optimized for airflow dynamics, while the drive mechanism allows for flexibility in operation, catering to different industrial needs. Together, these components ensure that Roots air blowers can deliver efficient air movement, making them an essential tool in various industrial processes.
Roots air blowers are widely used across various industries due to their ability to provide a consistent supply of compressed air. In wastewater treatment plants, for instance, these blowers play a crucial role in aeration processes, ensuring sufficient oxygen is available for microbial processes that break down organic matter. The reliability and efficiency of Roots air blowers make them ideal for maintaining optimal conditions in such systems, ultimately improving treatment outcomes.
In addition to wastewater treatment, Roots air blowers find applications in the pneumatic conveying of bulk materials in industries such as food processing and pharmaceuticals. Their capacity to move powders, granules, and other bulk solids with minimal damage ensures that products maintain their integrity during transit. Furthermore, they are also used in chemical plants for providing air or other gases needed in various reactions. The versatility of Roots air blowers allows for tailored solutions in different environments, contributing to enhanced productivity and operational efficiency across multiple sectors.
Roots blowers are widely recognized for their efficiency in various industrial applications, but understanding their performance metrics and maintenance considerations is crucial for optimizing their function. Efficiency in Roots blowers is primarily assessed through their volumetric and mechanical efficiency. Volumetric efficiency is the ratio of the actual flow rate to the theoretical flow rate, influencing how effectively the blower can move air or gas. Mechanical efficiency, on the other hand, examines the energy losses through friction and other factors within the system. It’s essential to regularly monitor these metrics to ensure that the blower operates within its optimal range, minimizing energy consumption and maximizing output.
Maintenance is another critical aspect that can significantly impact the performance of Roots blowers. Routine checks for wear and tear on critical components such as seals, rotors, and bearings are vital to prevent inefficiencies. Regular maintenance not only extends the lifespan of the blower but also enhances its reliability, reducing the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns and subsequent downtime in operations. Implementing a structured maintenance schedule and using appropriate lubricants can greatly contribute to maintaining high operational efficiency. Understanding these performance metrics and ensuring diligent maintenance practices will lead to improved operational outcomes in systems that utilize Roots blowers.
| Dimension | Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Air Flow Rate (CFM) | 100 - 5000 | Typical range for Roots blowers. |
| Efficiency (%) | 65 - 90 | Depends on operating conditions. |
| Operating Pressure (psi) | 0 - 15 | Common operating pressure range. |
| Noise Level (dB) | 70 - 90 | Requires soundproofing in some environments. |
| Maintenance Frequency (months) | 6 | Regular oil changes and inspections needed. |